In an AC circuit, there are two types of electrical power supplied to the load from the power supply: one is active power and the other is reactive power. When the load is resistive load, the power consumed is active power, when the load is capacitive or inductive load, the consumption is reactive power. Active power voltage and current in the same phase (AC power is the difference between active and reactive power), when the voltage exceeds the current, it’s inductive reactive power; when the current exceeds the voltage, it’s capacitive reactive power.
Active power is the electrical power required to keep the normal operation of electric equipment, that is, the conversion of electrical energy into other forms of energy (mechanical energy, light energy, heat) of electrical power. For example: 5.5 kilowatts of electric motor is 5.5 kilowatts of electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy, driving the pump to pump water or threshing machine threshing; various lighting equipment will be converted into light energy, for people to live and work lighting.
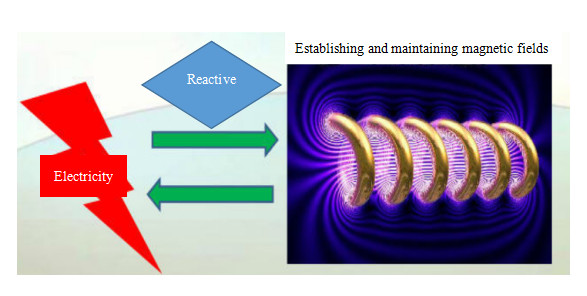
Reactive power is more abstract; it is the electrical power used for the exchange of electric and magnetic fields within a circuit and to establish and maintain the magnetic field in electrical equipment. It does not work externally, but is transformed into other forms of energy. Any electrical device with an electromagnetic coil consumes reactive power to establish a magnetic field. For example, a 40-watt fluorescent lamp requires more than 40 watts of active power (the ballast also needs to consume part of the active power) to emit light, but also requires about 80 reactive power for the ballast coil to establish an alternating magnetic field. Because it does not do external work, only to be called “reactive”.
Post time: Apr-06-2022